Horn
ELECTRIC HORNS
Horns are broadly classified as electric type or air type horns. Electric type horns are compact and efficient, and thus are used widely in ordinary passenger cars. Because air type horns have a large body and require compressed air, their use is restricted to large trucks and so on.
Electric horns can be divided by timbre into two types: the Flat Horn with a sharp and stimulating sound also called Disc Horn, and the Trumpet Shaped Horn with a softer sound also called Snail Horn. Because electric horns are not actuated externally, but instead adopt a mechanical self-excited vibration system, they excel in cost and are widely used.
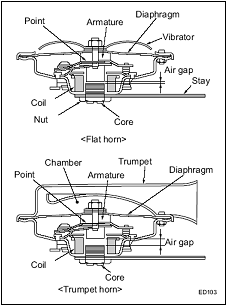
Electric horns are constructed of a diaphragm that generates sound, an armature (moving attraction part) connected to the diaphragm, a coil to generate the driving force, and a point (contact) that controls the flow of current through the coil. In addition, flat horns also have a vibrator that uses resonance to amplify sound, while trumpet horns use a trumpet to amplify sound in the same way.
How Horn Works
When the horn switch on the steering wheel is pressed, current flows from the battery through the coil, magnetizing the core and generating magnetomotive force.
- The armature is attracted, and the diaphragm moves.When the armature is attracted to a certain position, it presses the point down, and the contact opens.
- When the contact opens, current flowing through the coil is interrupted and the attraction disappears. The force of the diaphragm spring returns the armature, and the contact once again closes.
- This action is repeated approximately 400 times per second to vibrate the diaphragm and generate sound. The number of repeats is termed the fundamental frequency, and this determines the pitch of the sound (tone).
Differences Between A Disc Horn & Snail Horn
Flat Horn /Disc Horn
- Flat horns use a vibrator to amplify sound according to its resonance.
- Flat horns are constructed so that the air gap is narrow, and the armature collides with the core. The impact force generated from the collision creates higher harmonic components that resonate at a number of times the fundamental frequency, and this energy excites the vibrator, making it resonate and amplifying the sound pressure.
- Flat horns amplify by resonating this kind of mechanical collision force, so they have a sharp frequency characteristic and highly efficient amplification, making them the most compact type of horn. In addition, they have a sharp and stimulating timbre that is very effective for warnings
Trumpet Horn / Snail Horn
- Trumpet horns use the resonance of a trumpet to amplify sound.
- Because there is no need for the armature and core to collide as in a flat horn, trumpet horns have a wide air gap. The repeated vibrations of the diaphragm are converted to sound in the air chamber, and these sounds amplify as they resonate along the length of the trumpet.
- In contrast to the sharp peak frequency characteristic of flat horns, trumpet horns have wide and gradual frequency components, resulting in a soft-timbered sound
